- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
GM130 (cis-Golgi Marker) Antibody [A12L1]
Cat.No.: F2626
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Dog, Human, African green monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
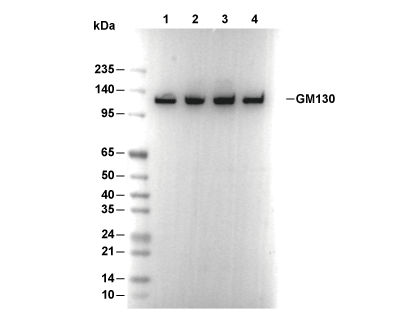
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 113 kDa 130 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human liver tissue; Human cervix carcinoma tissue; MCF7 cells; HeLa cells; COS-7 cells; MDCK(NBL-2) cells; ARPE-19 cells; MDCK(BL-1) cells; COS-1 cells; MDCK 2 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| GM130 (cis-Golgi Marker) Antibody [A12L1] detects endogenous levels of total GM130 (cis-Golgi Marker) protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| A12L1 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Golgin subfamily A member 2, 130 kDa cis-Golgi matrix protein, GM130 autoantigen, Golgin-95, GM130, GOLGA2 |
| Background |
|---|
| GM130, also known as Golgi matrix protein 130 kDa (GOLGA2), is a peripheral membrane protein and cis-Golgi marker that is critical for maintaining the structure of the Golgi ribbon and enabling vesicular trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum. This ~130 kDa protein localizes primarily to the cis-Golgi network, where its extended rod-like structure, rich in coiled-coil domains, mediates detergent- and salt-resistant oligomeric matrix assembly and peripheral Golgi association. GM130 recruits GRASP65 through direct interaction to organize cisternal stacking and mini-stack formation, processes essential for protein glycosylation, sorting, and transport through the secretory pathway; it also interacts with Rab1 and SNAREs such as syntaxin5 to guide vesicle tethering, docking, and fusion, and supports microtubule nucleation at Golgi outposts for polarized cargo movement. GM130 regulates not only Golgi architecture but also centrosome positioning, mitotic spindle organization, cell polarity, and migration via modulation of microtubule dynamics and acetylation, and ensures cell cycle fidelity by preventing multipolar spindle formation in p53-deficient contexts. Disruption of GM130 leads to Golgi fragmentation, impaired trafficking, and has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s (through effects on tau pathology and APP processing) and frontotemporal dementia. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.