- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
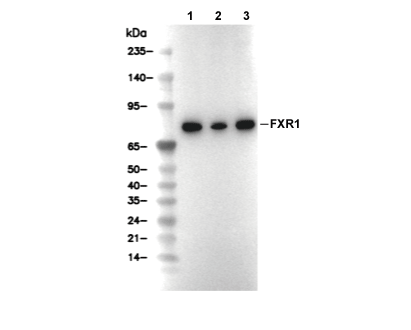
FXR1 Antibody [G5P16]
Cat.No.: F4738
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 78-84 kDa |
| Positive Control | Human skeletal muscle tissues; Mouse skeletal muscle tissues; 293 cells; NBT-11 cells; COS-7 cells; C2C12 cells; C2C12 cells (MG-132, 10 μg/mL, 3 h) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| FXR1 Antibody [G5P16] detects endogenous levels of total FXR1 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| G5P16 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| FXR1; RNA-binding protein FXR1; FMR1 autosomal homolog 1; hFXR1p |
| Background |
|---|
| FXR1 (Fragile X Mental Retardation Autosomal Homolog 1) is an RNA-binding protein in the fragile X-related family, closely related to FMRP and FXR2 with ~60% sequence identity across key exons, and is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of neurons, dendrites, and muscle, with knockout resulting in embryonic lethality in mice. Its structure includes two N-terminal Tudor domains for methyl-lysine recognition, a non-canonical nuclear localization signal (NLS, residues 114–150), a nuclear export signal (NES) in exon 12, a coiled-coil dimerization motif in exon 7 that links to 40S/60S ribosomes, tandem KH1/KH2 domains for binding GU-rich or G-quadruplex RNAs, and a C-terminal RGG box methylated by PRMT1 to regulate polysome association. FXR1 shuttles mRNAs from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to facilitate localized translation, represses GluA1 and GluA2 AMPA receptor subunits via 5’UTR elements for synaptic modulation, destabilizes p21 mRNA to promote neural stem cell proliferation, and interacts with CYFIP1/2, PAK1, GSK3β, and MRE11 in stress response signaling. Its regulatory mechanisms involve KH2-mediated auto-inhibition relieved by phosphorylation (by CK2, PAK1, or PKCι), GSK3β-induced degradation relevant to mood control, and post-translational modification by sumoylation or ubiquitination to modulate synaptic plasticity and stability in mGluR pathways and stress granules. Dysregulation of FXR1 contributes to fragile X syndrome via interactions with FMRP complexes, is linked to autism (through SNPs), schizophrenia and bipolar disorder (via AMPA signaling), and various cancers such as lung squamous cell carcinoma where it promotes proliferation through the ECT2/PRKCI axis. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.