- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Dynein intermediate chain 1/DNAI1 Antibody [E1A7]
Cat.No.: F3995
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Rat, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
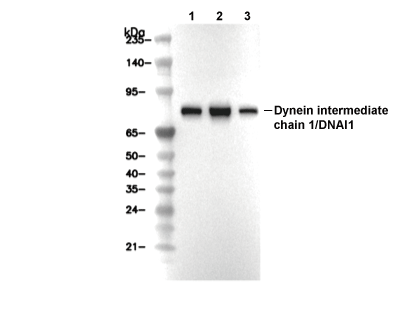
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 79 kDa 79 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human testis tissue; Rat testis tissue; Mouse testis tissue; Jurkat cells; F9 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Dynein intermediate chain 1/DNAI1 Antibody [E1A7] detects endogenous levels of total Dynein intermediate chain 1/DNAI1 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| E1A7 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Dynein axonemal intermediate chain 1; Axonemal dynein intermediate chain 1; DNAI1 |
| Background |
|---|
| Dynein intermediate chain 1 (DNAI1) is a WD-repeat protein that forms the structural base of outer dynein arms (ODAs) in motile cilia axonemes, assembling with heavy chains like DNAH5 and DNAH11 and various light chains. It features seven conserved WD40 propeller blades that undergo helical folding upon binding LC8 light chains, supporting microtubule attachment, while its flexible N-terminal domain coordinates cargo adaptor recruitment necessary for force generation during ATP-driven sliding between A/B tubule doublets. DNAI1 anchors ODAs at specific intervals along the axoneme perimeter, enabling coordinated power and recovery strokes required for mucociliary clearance in respiratory epithelia and for sperm flagellar propulsion. ODA assembly is mediated by intraflagellar transport, and DNAI1 mutations can disrupt ODA docking, resulting in static or immotile cilia with normal ultrastructure except for missing ODAs. Through DNAI1-LC8 interactions, conformational changes are transmitted from heavy chain AAA+ rings to microtubule-binding domains, regulating sliding velocity and displacement and preventing axonemal collapse. Disease-associated truncations that destabilize the WD40 propeller structure lead to primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), including Kartagener syndrome, which is characterized by situs inversus, neonatal respiratory distress, chronic rhinosinusitis, bronchiectasis, and male infertility due to impaired sperm motility. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.