- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
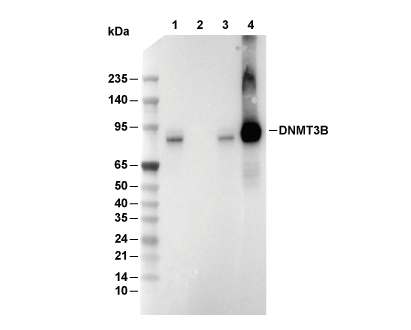
DNMT3B Antibody [K20B15]
Cat.No.: F4718
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 96 kDa |
| Positive Control | HCT 116 cells; K-562 cells; NCCIT cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | HEK 293 cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| DNMT3B Antibody [K20B15] detects endogenous levels of total DNMT3B protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| K20B15 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B; Dnmt3b; DNA methyltransferase HsaIIIB (DNA MTase HsaIIIB; M.HsaIIIB); DNMT3B |
| Background |
|---|
| DNMT3B is a critical de novo DNA methyltransferase responsible for establishing methylation patterns during early embryonic development, particularly at implantation, by targeting centromeric, pericentromeric, subtelomeric repeats, and intragenic regions of active genes to regulate gene expression, chromatin structure, and cellular differentiation. DNMT3B contains an N-terminal PWWP domain that binds H3K36me3 and regulates tetramer assembly, an ADD domain that recognizes unmethylated H3K4 tails to autoinhibit the catalytic methyltransferase (MTase) domain through intramolecular interactions while facilitating nucleosome core binding via acidic patch contacts, and a C-terminal MTase domain with a target recognition domain (TRD) that mediates DNA binding, homodimerization, and catalyzes methyl group transfer from S-adenosyl methionine to cytosine C5 at both CpG and non-CpG sites, often in concert with DNMT3A and DNMT3L for processive modification of nucleosomal linker DNA. DNMT3B collaborates with other DNMTs and chromatin factors such as HDACs and HP1 to drive epigenetic silencing, genomic imprinting, and heterochromatin maintenance, with its oligomerization and histone-tail sensing enabling context-specific targeting. The mechanistic interplay between PWWP and ADD domains relieves autoinhibition in response to H3K4me0/H3K36me3, promoting MTase access to DNA, while mutations—such as those seen in ICF syndrome- impair repeat methylation and cause chromosomal instability. Dysregulation of DNMT3B, including overexpression or pathogenic variants, contributes to diseases like ICF syndrome and various cancers by causing aberrant DNA hypermethylation or hypomethylation of tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.