- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
DNAJA1 Antibody [J3K12]
Cat.No.: F4809
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
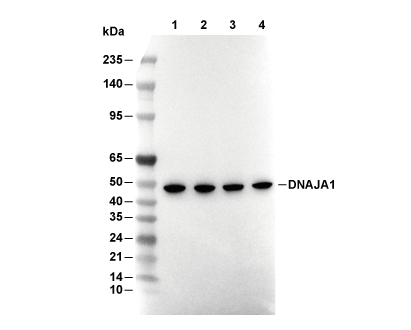
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 45 kDa 45 kDa, 49 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Jurkat cells; HepG2 cells; HEK293T cells; SKBR 3 cells; HAP1 cells; Jurkat cells; Raji cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| DNAJA1 Antibody [J3K12] detects endogenous levels of total DNAJA1 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| J3K12 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| DNAJ2; HDJ2; HSJ2; HSPF4; DNAJA1; DnaJ homolog subfamily A member 1; DnaJ protein homolog 2; HSDJ; Heat shock 40 kDa protein 4; Heat shock protein J2; Human DnaJ protein 2; HSJ-2; hDj-2 |
| Background |
|---|
| DNAJA1 (DnaJ homolog subfamily A member 1) is a cytosolic type I Hsp40 co-chaperone essential for proteostasis and stress signaling. It features an N-terminal J-domain (residues 4–70, with an HPD motif at His33-Pro34-Asp35 crucial for Hsp70 ATPase stimulation), a C4 zinc finger domain (aa 78–115, containing eight cysteines that coordinate two Zn²⁺ ions to probe hydrophobic patches on client proteins), a glycine/phenylalanine-rich flexible linker (aa 116–165), and a C-terminal substrate-binding domain (aa 166–397) comprising stacked β-sheets and α-helices, plus a farnesylated CTIL355–358 motif for dynamic tethering to the ER or plasma membrane. In the Hsp70 chaperone cycle, the J-domain’s α-helix II docks to Hsp70’s nucleotide-binding domain, accelerating ATP hydrolysis over 1000-fold and trapping substrates in the ADP-bound state. The zinc fingers deliver clients such as conformational mutant p53 (where DNAJA1 binds the mutp53 core domain to sterically block CHIP E3 ubiquitination at Lys620, stabilizing oncogenic conformers that drive pancreatic and cholangiocarcinoma invasion via Cdc42/Rac1-mediated filopodia), CFTR ΔF508 (directing triage for ER retention and retrotranslocation via Hsc70), tau fibrils (facilitating Hsp104-independent disaggregation), and influenza PB2/PA nuclear import complexes. DNAJA1 also restrains JNK/c-Jun hyperactivation under oxidative and ER stress by promoting Hsc70-mediated SAPK sequestration, thereby preventing BAX-mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Additionally, it modulates polyQ-htt aggregation in Huntington’s models and hERG channel trafficking. DNAJA1 downregulation in PDAC tumors paradoxically increases mutp53 persistence and tumor growth, sensitizing these tumors to J-domain inhibitors (such as A11, which targets Y7/K44/Q47 to disrupt mutp53 interaction and promote its proteasomal clearance). |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.