- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Dicer Antibody [F18A13]
Cat.No.: F4018
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
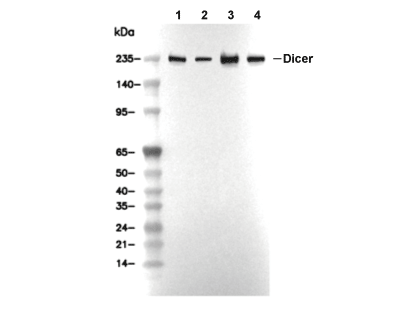
| Observed MW |
|---|
| 250 kDa,124 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Mouse testis tissue; Rat testis tissue; Mouse cerebrum tissue; Human testis tissue; Human brain tissue; A549 cells; HepG2 cells; HeLa cells; HEK-293 cells; HAP1 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | Human skeletal muscle tissue; Rat skeletal muscle tissue; Mouse skeletal muscle tissue |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Dicer Antibody [F18A13] detects endogenous levels of total Dicer protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| F18A13 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| DICER, HERNA, KIAA0928, DICER1, Endoribonuclease Dicer, Helicase with RNase motif, Helicase MOI |
| Background |
|---|
| Dicer is an essential RNase III endoribonuclease that cleaves double-stranded RNAs and primary microRNAs (pri-miRNAs) into ~22-nucleotide mature miRNAs and siRNAs, which are loaded into Argonaute proteins within the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to mediate post-transcriptional gene silencing through mRNA cleavage or translational repression, thereby critically regulating development, differentiation, and cellular stress responses. This approximately 220 kDa L-shaped enzyme consists of an N-terminal DExD/H helicase domain that drives ATP-dependent translocation of dsRNA, two RNase III domains that perform precise endonucleolytic cuts via Mg²⁺-coordinated catalysis about 22 nucleotides from the termini using a molecular ruler mechanism, a dsRNA-binding domain that clamps and orients substrates, and accessory motifs such as the DUF283 platform that help position pre-miRNAs for Drosha-processed stem-loops. Cofactors like TRBP and PACT enhance the fidelity of Dicer processing by stabilizing the enzyme-substrate complex. The helicase domain powers polar threading of dsRNA (~2 base pairs per ATP hydrolyzed), aligning the termini into the RIIIa and RIIIb active sites separated by approximately 65 angstroms for synchronized phosphodiester hydrolysis, which yields miRNA/miRNA* duplexes; intrinsic unwinding mechanisms then enable product release. Dysregulation of Dicer, whether by somatic mutations, haploinsufficiency, or viral inhibition, leads to global loss of miRNAs, promoting oncogenesis (as seen in leukemia and glioblastoma), neurodegeneration, and autoimmunity due to impaired RNA interference defense. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.