- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
DHX9 Antibody [E8M24]
Cat.No.: F5128
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Mouse Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
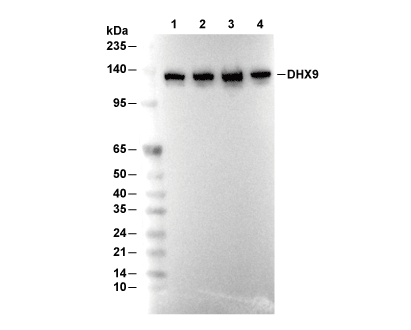
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 141 kDa 140 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Mouse brain tissue; MCF7 cells; HeLa cells; HEK-293 cells; HepG2 cells; Jurkat cells; K-562 cells; THP-1 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| DHX9 Antibody [E8M24] detects endogenous levels of total DHX9 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| E8M24 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| DHX9; ATP-dependent RNA helicase A; EC:3.6.4.13; DEAH box protein 9; DExH-box helicase 9; Leukophysin (LKP); Nuclear DNA helicase II (NDH II); RNA helicase A; DDX9; LKP; NDH2 |
| Background |
|---|
| DHX9 (DExH-box helicase 9, also known as RNA helicase A or nuclear DNA helicase II) is a 1,200-amino-acid SF2 family helicase that is ubiquitously expressed and essential for embryonic development, functioning to unwind DNA and RNA structures in the 3'-5' direction using all NTPs and dNTPs as energy sources. Its core consists of RecA-like helicase domains (motifs I–VI, residues ~380–830) that form an NTP-binding cleft with a flexible hinge, flanked by N-terminal double-stranded RNA-binding domains (dsRBD1/2) for substrate recognition, a minimal transactivation domain (MTAD) for RNA polymerase II association, and C-terminal helicase-associated (HA2), OB-fold, and RGG-box motifs that specifically recognize G-quadruplexes and R-loops. The dsRBD2 domain stabilizes the RNA channel, while the OB-fold and RGG-box grip single-stranded nucleic acid tails; the protein undergoes conformational shifts between an inactive, closed state (with disordered dsRBD2) and an active, open, RNA-anchored state triggered by NTP and RNA binding. DHX9 resolves R-loops by recruiting TDRD3 to prevent replication stress and double-strand breaks, unwinds G-quadruplexes and inverted repeats (IRAlus) to suppress circRNA biogenesis, facilitates BRCA1 recruitment for homologous recombination repair, promotes pre-mRNA splicing through interactions with U2AF65 and SRSF1, and coactivates c-Myc and STAT6 transcription. NTP hydrolysis drives 3'-tail anchored translocation and remodeling of RNA:DNA hybrids and multi-stranded complexes, with the dsRBD2/RecA2 β-hairpin gripping RNA backbones and OB/HA2 rotation opening channels for complex nucleic acid substrates. Dysregulation of DHX9 is implicated in cancer (upregulated in HCC and breast cancer, promoting angiogenesis and invasion via VEGF and c-Myc), viral replication (through enhancer binding in HIV and JCV), and neurodegeneration (due to unresolved G-quadruplex toxicity). |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.