- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
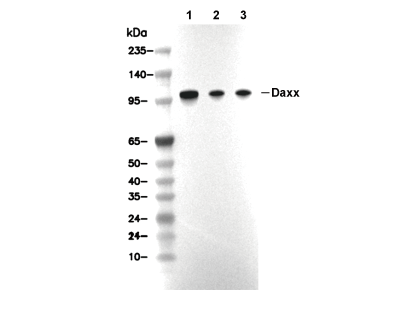
Daxx Antibody [H1F20]
Cat.No.: F4690
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 110 kDa |
| Positive Control | K562 cells; A20 cells; PC12 cells; HeLa cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Daxx Antibody [H1F20] detects endogenous levels of total Daxx protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| H1F20 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| DAXX; Death domain-associated protein 6; Daxx (hDaxx); ETS1-associated protein 1 (EAP1); Fas death domain-associated protein; BING2; DAP6 |
| Background |
|---|
| Daxx (Death domain-associated protein) is a ubiquitously expressed nuclear scaffold protein, initially identified as a Fas-interactor, that primarily localizes to promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies (PML-NBs) and is essential for chromatin remodeling, transcriptional regulation, and apoptosis modulation; knockout of Daxx in mice leads to embryonic lethality due to excessive developmental apoptosis. Daxx contains an N-terminal helical bundle (4HB) domain that mediates interactions with partners such as ATRX, p53, and MDM2; a central H3.3/H4-binding region that folds with histone dimers to function as an H3.3-specific chaperone, depositing H3.3 at PML-NBs and telomeres; poly-Asp/Glu (polyD/E) motifs that sense misfolded proteins and facilitate their refolding; two SUMO-interaction motifs (SIMs) that regulate sumoylation and PML-NB targeting; and a C-terminal domain that associates with Fas, CENP-C, and DNA methyltransferases. Daxx facilitates ATRX-dependent H3.3 deposition for heterochromatin silencing and telomere maintenance, assembles the telomerase holoenzyme in Cajal bodies via N-terminal interactions with TERT subunits (DKC1, GAR1, NHP2) to promote telomerase targeting and prevent telomere shortening, represses transcription of NF-κB and E2F-1 targets through HDAC recruitment and PML-NB scaffolding, modulates apoptosis via Fas/JNK activation while exhibiting anti-apoptotic effects during development, and responds to cellular stress by binding misfolded proteins to maintain proteostasis. Disease-associated mutations in Daxx disrupt binding to partners, such as impairing H3.3/ATRX-mediated deposition or blocking telomerase assembly via N-terminal lesions, while post-translational sumoylation enhances PML targeting, phosphorylation modulates subnuclear localization, and interactions with HIPK2 and TGF-β pathways integrate signals for cell cycle control and survival. Dysregulation of Daxx contributes to cancer through H3.3 perturbations that promote oncogene expression, to alpha-thalassemia syndromes via ATRX mutations, and to neurodegenerative diseases due to failures in proteostasis. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.