- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
CYR61 Antibody [M15N8]
Cat.No.: F4714
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHC |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
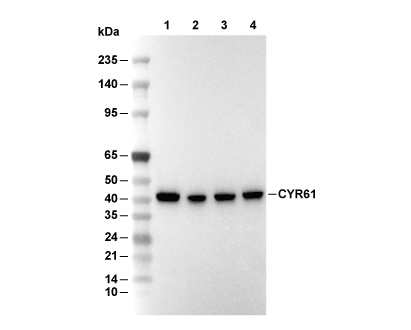
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 41 kDa |
| Positive Control | Human urothelial carcinoma; Human lung adenocarcinoma; Human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; Human prostate adenocarcinoma; OVCAR8 cells; HeLa cells; Saos-2 cells; C2C12 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | MCF7 cells; HT-29 cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| CYR61 Antibody [M15N8] detects endogenous levels of total CYR61 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| M15N8 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| CCN1; CCN family member 1; Cellular communication network factor 1; Cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61; Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 10 (IBP-10; IGF-binding protein 10; IGFBP-10); Protein CYR61; Protein GIG1; CYR61; GIG1; IGFBP10 |
| Background |
|---|
| Cysteine-rich protein 61 (CYR61, also known as CCN1) is a secreted matricellular protein of the CCN family distinguished by its high cysteine content forming disulfide bonds that stabilize its structure, featuring four conserved modular domains from N- to C-terminus: an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-like domain (Module I) with 68 amino acids for low-affinity IGF interactions, a von Willebrand factor type C repeat (vWC) domain (Module II) involved in dimerization and heparin binding, a thrombospondin type 1 repeat (TSP-1) domain (Module III) critical for integrin αvβ3 and α6β1 engagement, and a C-terminal cysteine-knot domain (Module IV) mediating receptor binding and multimerization on the extracellular matrix. CYR61 orchestrates diverse context-dependent cellular responses by binding distinct integrins and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) like syndecan-4, promoting angiogenesis through αvβ3-mediated endothelial proliferation, VEGF upregulation, and recruitment of CD34+ progenitors while inducing apoptosis via α6β1/HSPG complexes that trigger ROS production via RAC-1, 5-lipoxygenase, NADPH oxidase, and mitochondria, leading to sustained JNK activation, c-FLIP degradation, caspase-8/10 signaling, and p53-mediated DNA damage responses in fibroblasts and endothelial cells. It drives cardiovascular and skeletal development including placental vessel bifurcation, hypertrophic cartilage neovascularization, osteoblast differentiation via αvβ3/ILK, and osteoclast inhibition, whereas in tumorigenesis its overexpression correlates with progression in breast, lung, and hepatocellular carcinoma via Wnt/β-catenin or hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulation, yet inversely with prostate cancer aggressiveness. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.