- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
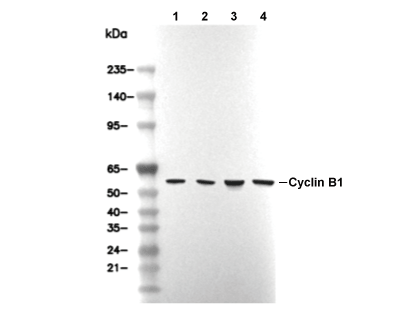
Cyclin B1 Antibody [C9G10]
Cat.No.: F0884
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 55 kDa |
| Positive Control | HT-29 cells; HeLa cells; Jurkat cells; HCT 116 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Cyclin B1 Antibody [C9G10] detects endogenous levels of total Cyclin B1 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| C9G10 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| G2/mitotic-specific cyclin-B1; CCNB1; CCNB |
| Background |
|---|
| Cyclin B1 is the essential regulatory subunit of the mitosis-promoting factor (MPF) complex, forming a functional unit with CDK1 that accumulates during late G2 phase to trigger the G2/M transition in the cell cycle. Its cyclin box domain, a conserved α-helical structure, binds CDK1 and induces a conformational change that activates the kinase's catalytic cleft, exposing the active site for substrate phosphorylation. The N-terminal cytoplasmic retention signal (CRS) of cyclin B1, which contains multiple phosphorylation sites, regulates its nuclear shuttling; PLK1-mediated phosphorylation of these sites overrides inhibitory phosphates placed on CDK1 by Wee1, allowing nuclear localization and full MPF activation. This precise docking enables CDK1 to phosphorylate a wide array of substrates critical for mitotic entry, such as nuclear lamins for envelope breakdown, condensins for chromosome condensation, histone H1 for chromatin compaction, ECT2 for spindle and cytokinesis regulation, and APC/C activators for timely cyclin B1 degradation during anaphase. Cyclin B1-CDK1 complexes also localize to nuclear pore complexes by binding MAD1, coordinating NPC disassembly with kinetochore recruitment for spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) signaling and ensuring genomic stability. Disruption of cyclin B1 levels or localization impairs these regulatory loops, leading to chromosomal instability and tumorigenesis in cancers where persistent MPF activity can bypass SAC-mediated arrest. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.