- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
CNBP Antibody [E10D2]
Cat.No.: F5127
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Rat, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Mouse Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
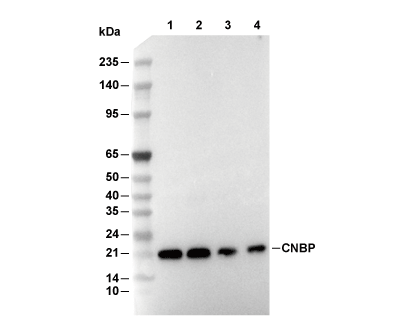
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 19 kDa 19-25 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | LNCaP cells; HeLa cells; HepG2 cells; Jurkat cells; K-562 cells; HSC-T6 cells; PC-12 cells; NIH/3T3 cells; Neuro-2a cells; HEK-293 cells; HT-29 cells; 4T1 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| CNBP Antibody [E10D2] detects endogenous levels of total CNBP protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| E10D2 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| CNBP; CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein; Cellular nucleic acid-binding protein (CNBP); Zinc finger protein 9; RNF163; ZNF9 |
| Background |
|---|
| CNBP (ZNF9) is a highly conserved CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid-binding protein critical for embryonic development and post-transcriptional gene regulation, characterized by seven tandem zinc knuckle motifs that coordinate zinc ions to form compact ββα folds, enabling high-affinity binding to G-rich single-stranded DNA and RNA sequences. The presence of an RGG box between the first and second zinc fingers facilitates the formation of phase-separated biomolecular droplets and enhances cooperative nucleic acid remodeling. CNBP functions as a G-quadruplex (G4) chaperone, actively unfolding stable G4 structures within the c-Myc promoter to promote RNA polymerase II transcription, and within the 5'UTR of ODC mRNA to facilitate cap-independent translation. CNBP can transactivate genes such as β-catenin and IL-6 through direct, G4-dependent promoter binding, with its activity and localization dynamically regulated by phosphorylation-triggered dimerization and nuclear translocation in response to cellular stress and cytokine signaling. Expansion of (CCTG)n repeats in CNBP intron 1 underlies myotonic dystrophy type 2 (DM2), where mutant RNA transcripts sequester functional CNBP, resulting in muscleblind-like protein toxicity, impaired myogenesis due to myf5 G4 stabilization, and progressive multisystem atrophy |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.