- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
CD45 Antibody [M13C14]
Cat.No.: F4022
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHC, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
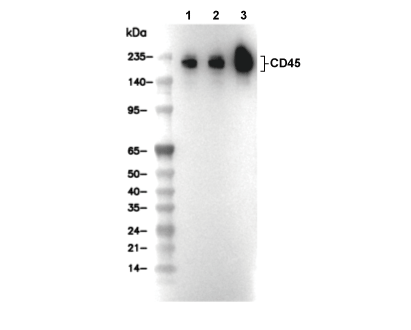
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 147 kDa 200 kDa, 160-220 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Normal kidney tissue; Normal colon lymphoid cells tissue; Human tonsil; Normal spleen tissue; Jurkat cells; Raji cells; HuT-78 cells; PBMCs; THP-1 cells; MCF7 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | Skeletal muscle tissue; 293T cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| CD45 Antibody [M13C14] detects endogenous levels of total CD45 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| M13C14 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| CD45, PTPRC, Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C, Leukocyte common antigen, T200, L-CA |
| Background |
|---|
| CD45, a type I transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase encoded by PTPRC, is abundantly expressed on all hematopoietic cells except erythrocytes and platelets. It features a heavily glycosylated extracellular domain with variable isoforms generated through alternative splicing of specific exons, resulting in fibronectin type III-like motifs that influence its functional diversity. A single transmembrane helix connects this extracellular portion to a cytoplasmic region containing two tandem PTP domains: the membrane-proximal D1 domain, which is catalytically active and harbors the signature CX5RTG motif essential for substrate dephosphorylation, and the membrane-distal D2 domain, which serves regulatory or inhibitory functions, followed by a C-terminal tail involved in substrate interactions. CD45 regulates antigen receptor signaling by dephosphorylating Src family kinases such as Lck and Fyn at their inhibitory C-terminal tyrosines to promote kinase activation and basal TCR/CD3 signaling, while also targeting activating tyrosines or ITAM motifs to restrain excessive signaling. It further influences integrin-mediated adhesion, chemokine responsiveness, and cytoskeletal dynamics via modulation of SFK, JAK, and STAT pathways. CD45 is critical for T and B cell development, setting activation thresholds, cytokine production, thymocyte selection, and both innate and adaptive immune responses, also contributing to apoptosis resistance. Distinct isoforms like CD45RO play specialized roles, such as supporting memory T-cell synapse formation. Dysregulation of CD45 through mutations, splicing alterations, or overexpression is linked to immunodeficiencies like SCID, autoimmune diseases such as SLE, hematological malignancies, and transplant rejection. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.