- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Artemis Antibody [H20J21]
Cat.No.: F1506
Application:
Reactivity:
Experiment Essentials
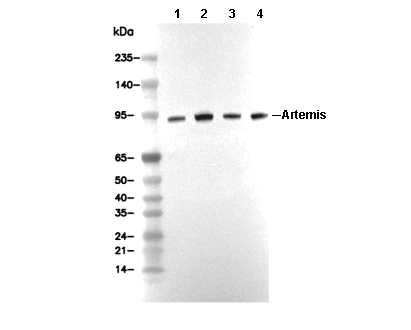
WB
Exposure time of at least 60s is recommended.
Exposure time of at least 60s is recommended.
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 90 kDa |
| Positive Control | Jurkat cell; HT-29 cell; MCF7 cell |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Exprimental Methods
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 6. Add protein loading buffer, heat 20 μL of the sample at 95~100°C for 5 min, let it cool down on ice and then centrifuge for 5 min. Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. (Exposure time of at least 60s is recommended) |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Artemis Antibody [H20J21] detects endogenous levels of total Artemis protein. |
| Subcellular Location |
|---|
| Nucleus |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| Q96SD1 |
| Clone |
|---|
| H20J21 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Protein artemis; DNA cross-link repair 1C protein; Protein A-SCID; SNM1 homolog C; hSNM1C; SNM1-like protein; DCLRE1C; ARTEMIS; ASCID; SCIDA; SNM1C |
| Background |
|---|
| Artemis (DCLRE1C, also known as SNM1C) is a ubiquitously expressed nuclear nuclease belonging to the metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) superfamily, essential for non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) DNA repair and V(D)J recombination in developing lymphocytes. Artemis is a 692-amino-acid protein with an N-terminal catalytic domain (residues 1-360) comprising a core MBL fold (α/β-β/α sandwich) and embedded β-CASP subdomain containing conserved motifs 1-4 (His33, His35, His115, Asp116 coordinating Zn²⁺ ions M1/M2) and motifs A-C for nucleic acid processing, plus a largely unstructured C-terminal regulatory tail (residues 361-692) that autoinhibits activity and mediates DNA-PKcs tethering. DNA-PKcs phosphorylates Artemis (e.g., at Thr127, Ser251) upon DSB recognition, activating its structure-specific endonuclease activity to open hairpin-sealed coding ends in V(D)J recombination, trim 5'/3' overhangs, flaps, and bubbles in NHEJ for XRCC4/LIG4 ligation, and process IR-induced complex ends while antagonizing HR via 53BP1-PTIP interaction. ATM/ATR further phosphorylate Artemis for G2/M and S-phase checkpoint recovery, promoting Cdk1-cyclin B activation and cyclin E degradation via SCF^{Fbw7}. Biallelic mutations cause radiosensitive severe combined immunodeficiency (RS-SCID) with defective V(D)J joining and genome instability predisposing to malignancy. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.