- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Antibody [G21H2]
Cat.No.: F4674
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, IF, FCM, ChIP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 11 kDa |
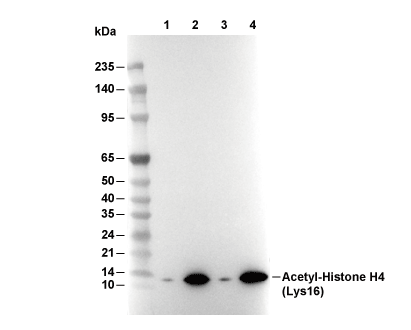
| Positive Control | Human ductal breast carcinoma; Human prostate carcinoma; Human esophageal carcinoma; Human urothelial carcinoma; Human colon carcinoma; Human squamous cell lung carcinoma; Human skin; Human spleen; Human testis; A20 syngeneic tumor; Mouse colon; Mouse testis; Mouse endometrium; Human colon carcinoma; T-47D cells (TSA, 1μM, 6 h); HeLa cells (TSA, 1μM, 18 h); C2C12 cells (TSA, 1μM, 18 h); C6 cells (TSA, 1μM, 18 h) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Antibody [G21H2] detects endogenous levels of total Histone H4 protein only when it is Acetylated at Lys16. |
| Clone |
|---|
| G21H2 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| H4C1; H4/A; H4FA; HIST1H4A; H4C2; H4/I; H4FI; HIST1H4B; H4C3; H4/G; H4FG; HIST1H4C; H4C4; H4/B; H4FB; HIST1H4D; H4C5; H4/J; H4FJ; HIST1H4E; H4C6; H4/C; H4FC; HIST1H4F; H4C8; H4/H; H4FH; HIST1H4H; H4C9; H4/M; H4FM; HIST1H4I; H4C11; H4/E; H4FE |
| Background |
|---|
| Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) is an epigenetic modification on the N-terminal tail of histone H4 that neutralizes the positive charge of lysine 16 through acetyl transfer catalyzed by HAT1 and MOF. This modification disrupts the electrostatic interaction between H4K16 and the H2A acidic patch, preventing chromatin fiber compaction and maintaining an open euchromatin conformation favorable for transcriptional activation. The acetylation of H4K16 creates a bromodomain docking site that recruits the SAS chromatin assembly complex and antagonists of Sir proteins at telomeres, helping to establish boundaries between heterochromatin and euchromatin. H4K16ac inhibits ACF remodeling enzyme activity on compacted chromatin fibers and uniquely abolishes H4 tail-mediated internucleosomal interactions compared to other acetylation sites. H4K16ac regulates gene expression, DNA repair, and chromatin remodeling by facilitating transcription factor and promoter access and by preventing the spread of Sir2/3/4 silencing complexes into euchromatic regions. H4K16ac marks accessible chromatin at sites of apoptosis-associated cleavage and regulates differentiation programs in neutrophils. Hyperacetylation of H4K16 is associated with embryonic lethality and male sterility in Sas2 mutants and contributes to cancer progression by maintaining sustained euchromatin domains. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.