research use only
Sulfacetamide sodium salt hydrate Autophagy chemical
Cat.No.S4750
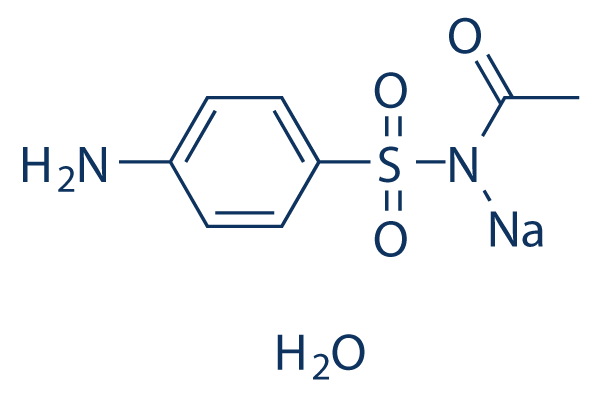
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 254.24
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CXCR Nrf2 Mitophagy LRRK2 ULK FKBP Heme Oxygenase cGAS LC3 Cell wall |
|---|---|
| Other Autophagy Inhibitors | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) Spautin-1 PIK-III DC661 Lys05 Autophinib Spermidine SMER28 EN6 Flubendazole |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 50 mg/mL
(196.66 mM)
Water : 50 mg/mL Ethanol : 2 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 254.24 | Formula | C8H9N2O3S.H2O.Na |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 6209-17-2 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC(=O)[N-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)N.O.[Na+] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
DHPS
9.5 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Sulfacetamide inhibits Arabidopsis DHPS with IC50 of 9.5 μM, pKa=5.4. Sulfacetamide induces anti-proliferative effects on T-47D cells and it is independent of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Sulfacetamide treatment lowers expression of p53/DRAM pathway in parallel with upregulation of Akt/mTOR pathway promoting cytoprotective autophagy. The LD50 of sulfacetamide in T-47D cells after 48 h is 41 mM. Sulfacetamide does not cause DNA fragmentation. In cells treated with sulfacetamide, the ATG5 expression level increases suggesting an increase in autophagosome formation in the autophagy pathway. Autophagy induction in the sulfathiazole and sulfacetamide treatments is not accompanied by apoptosis and occurred without any distinctive arrest in a phase of the cell cycle. It triggers autophagy in T-47D cells via a DAPK independent pathway. Sodium sulfacetamide or sulfacetamide is a bacteriostatic agent that is active against sulfonamide-sensitive Gramnegative and Gram-positive bacteria, including Streptococci, Staphylococci, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas pyocyanea, Salmonella spp., Proteus vulgaris, and Nocardia, which are usually isolated in secondary infections of the skin. Sulfacetamide inhibits mannose-6-phosphate isomerase (also known as phosphomannose isomerase (PMI)), which is considered the key enzyme in kinetoplastid energy metabolism.
|
| In vivo |
The LD50 of sulfacetamide for mice is 16,500 mg/kg by the oral route. In humans, the side effects include erythema, moderate swelling, nausea, vomiting, and headache. In addition to these side effects, the occurrence of StevensJohnson syndrome is reported in HIV-positive patients who received sulfacetamide drops for eye infections. All of these side effects, however, are associated with oral administration or high drug absorption through the skin, mucous membranes, and the conjunctiva, whereas topical use is not associated with strong side effects.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































