- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
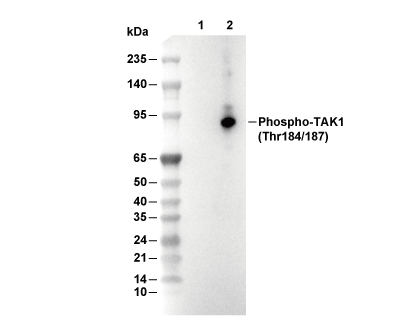
Phospho-TAK1 (Thr184/187) Antibody [G4C5]
Cat.No.: F0402
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 82 kDa |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Phospho-TAK1 (Thr184/187) Antibody [G4C5] detects endogenous levels of total TAK1 protein only when it is phosphorylated at Thr184/187. |
| Clone |
|---|
| G4C5 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7; Transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TGF-beta-activated kinase 1); MAP3K7; TAK1 |
| Background |
|---|
| Phospho-TAK1 (Thr184/187) is the activated form of the serine/threonine kinase TAK1 (MAP3K7), marked by dual phosphorylation within the activation T-loop of its N-terminal kinase domain. This modification is induced by TAB1 binding, which relieves autoinhibition and promotes autophosphorylation, stabilizing TAK1’s active conformation necessary for transmitting innate immune and stress signals. The phosphorylation sites are located between the conserved DFG and APE motifs, ensuring precise ATP binding and substrate access. TAB2 and TAB3 further enhance TAK1 activation by recruiting ubiquitin chains from TRAF6, amplifying signal transduction. Activated phospho-TAK1 serves as a central node for TNF-α, IL-1, and TGF-β pathways, directly phosphorylating IKKβ to trigger NF-κB nuclear translocation and proinflammatory cytokine production, as well as activating MKK4/6/7 to drive JNK and p38 MAPK cascades that regulate apoptosis, survival, and inflammation. Phosphorylation at Thr184/187 is essential for IL-1-induced NF-κB and AP-1 synergy and for optimal IL-6 expression, as mutations at these sites abolish downstream activation even in the presence of TAB1, while phospho-mimetic mutants hyperactivate these pathways. Hyperactive phospho-TAK1 at these residues sustains chronic NF-κB signaling in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and cancer, while selective inhibition of Thr184/187 phosphorylation disrupts TAK1 signalosome assembly, suppressing inflammatory cytokine storms and tumor progression. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.