- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Phospho-TAK1 (Ser439) Antibody [F17C11]
Cat.No.: F2613
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
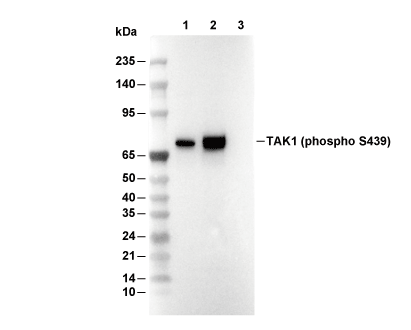
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 67 kDa 75 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Phospho-TAK1 (Ser439) Antibody [F17C11] detects endogenous levels of total TAK1 protein only when it is phosphorylated at Ser439. |
| Clone |
|---|
| F17C11 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| TAK1; MAP3K7; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7; Transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1; TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 |
| Background |
|---|
| Phospho-TAK1 (Ser439) is the activated form of transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), a serine/threonine kinase encoded by MAP3K7 that assembles with regulatory subunits TAB1, TAB2, and TAB3 to coordinate stress-responsive intracellular signaling. TAK1 contains a kinase domain with critical activation loop residues and a C-terminal Ser439 site, whose autophosphorylation is essential for achieving full catalytic activity following initial ubiquitin-dependent activation. This modification stabilizes TAK1 and enhances its recruitment to polyubiquitin chains through TAB2 and TAB3, facilitating downstream phosphorylation events. Active TAK1 propagates signaling through multiple major pathways, including the NF-κB pathway via IKK complex phosphorylation, JNK and p38 MAPK cascades through MAP2K activation, and ERK signaling. These pathways collectively regulate innate immunity, inflammation, cell survival, apoptosis, embryonic development, and cellular responses to cytokines such as IL-1, TGF-β, TNF-α, and TLR ligands. Phosphorylation at Ser439 is particularly important for promoting TAK1-dependent activation of transcription factors like AP-1 and NF-κB, and dysregulation of this signaling node is implicated in inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and various cancers. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.