research use only
Phospho-STAT3 (Ser727) Antibody [J17G14]
Cat.No.: F4695
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 86 kDa |
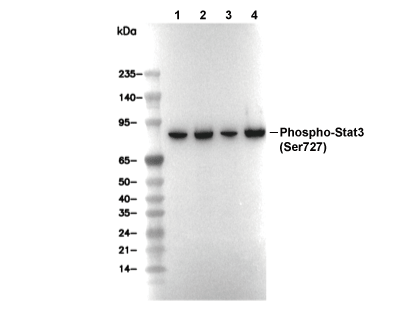
| Positive Control | 293 IL-1R cells (IL-1, 10 min); HeLa cells (hIL-1β, 10 min) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | 293 IL-1R cells |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Phospho-STAT3 (Ser727) Antibody [J17G14] detects endogenous levels of total STAT3 protein only when it is phosphorylated at Ser727. |
| Clone |
|---|
| J17G14 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Acute-phase response factor; STAT3; APRF |
| Background |
|---|
| Phospho-STAT3 (Ser727) is the serine-phosphorylated form of the STAT3 transcription factor, which is activated downstream of cytokine and growth factor signaling. This modification occurs within the C-terminal transactivation domain, specifically in a flexible loop adjacent to Pro715, and is mediated by MAPK and mTOR pathways after initial Tyr705 phosphorylation, dimerization, and nuclear translocation of STAT3. Ser727 phosphorylation accelerates dephosphorylation of Tyr705 by recruiting the TC45 phosphatase, enabling rapid activation-inactivation cycles necessary for proper interleukin-6 signaling. This phosphorylation event destabilizes dimer contacts and weakens both intermolecular and intramolecular interactions within the C-terminal tail, facilitating CRM1-independent nuclear export and preventing sustained STAT3 signaling. Dynamic regulation through Ser727 phosphorylation ensures precise temporal control of target gene expression, including genes such as socs3 and saa1. Changes such as the S727A mutation or N-terminal tagging can disrupt this regulatory cycling, resulting in nuclear accumulation and delayed reactivation of STAT3. In cancer, phospho-STAT3 (Ser727) can drive distinct gene expression programs independently of Tyr705 phosphorylation, as seen in clear cell renal carcinoma, while chronic hyperactivation of Ser727 phosphorylation contributes to inflammation and autoimmunity through dysregulated NF-κB and AP-1 crosstalk. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.