research use only
Phospho-PKR (Thr451) Antibody [C9J9]
Cat.No.: F2372
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Pig |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 62 kDa 68 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
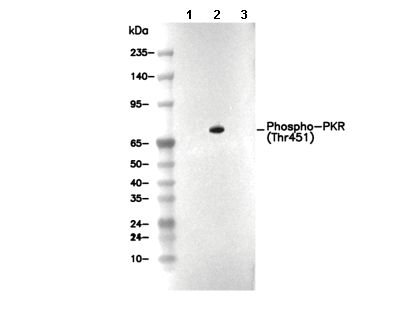
| Positive Control | HeLa cell (IFN α1, 1000U/ml ,18 h and then Calyculin A, 100nM, 15 min at 20 µg) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Exprimental Methods
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution ( recommending 5% BSA solution)
for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Phospho-PKR (Thr451) Antibody [C9J9] detects endogenous levels of PKR protein only when phosphorylated at Thr451. |
| Subcellular Location |
|---|
| Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| P19525 |
| Clone |
|---|
| C9J9 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| PKR, PRKR, EIF2AK2, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 2, Interferon-inducible RNA-dependent protein kinase, P1/eIF-2A protein kinase, Protein kinase RNA-activated, Tyrosine-protein kinase EIF2AK2, p68 kinase, eIF-2A protein kinase 2, Protein kinase R |
| Background |
|---|
| Protein kinase R (PKR) is an interferon-induced serine/threonine kinase that plays a central role in innate antiviral defense and regulation of cell growth. Structurally, PKR contains two tandem dsRNA-binding motifs at its N-terminus, a flexible linker, and a C-terminal kinase domain that adopts a bilobal fold. PKR expression is upregulated by interferons and it becomes activated upon binding viral dsRNA, which promotes dimerization and autophosphorylation. Among several phosphorylation sites, threonine 451 (Thr451) in the activation loop is critical for enzymatic activity, as mutation of this residue impairs PKR function. Phosphorylation at Thr451, together with Thr446, stabilizes the active conformation, enhances dimerization, and enables PKR to phosphorylate eIF2α at serine 51, thereby blocking translation initiation and suppressing viral replication. Thus, PKR phosphorylation, particularly at Thr451, is essential for its role in antiviral immunity and tumor suppressor functions. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.