- Inhibitors
- By product type
- Natural Products
- Inducing Agents
- Peptides
- Antibiotics
- Antibody-drug Conjugates(ADC)
- PROTAC
- Hydrotropic Agents
- Dyes
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
By research - Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- Featured Products
- MRTX1133
- Nab-Paclitaxel
- KP-457
- IAG933
- RMC-6236 (Daraxonrasib)
- RMC-7977
- Zoldonrasib (RMC-9805)
- GsMTx4
- Navitoclax (ABT-263)
- TSA (Trichostatin A)
- Y-27632 Dihydrochloride
- SB431542
- SB202190
- MK-2206 Dihydrochloride
- LY294002
- Alisertib (MLN8237)
- XAV-939
- CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib)
- Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1)
- Thiazovivin (TZV)
- CP-673451
- Verteporfin
- DAPT
- Galunisertib (LY2157299)
- MG132
- SBE-β-CD
- Tween 80
- Bavdegalutamide (ARV-110)
- Z-VAD-FMK
- Wnt-C59 (C59)
- IWR-1-endo
- (+)-JQ1
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) Hydrochloride
- RepSox (E-616452)
- Erastin
- Q-VD-Oph
- Puromycin Dihydrochloride
- Cycloheximide
- Telaglenastat (CB-839)
- A-83-01
- Ceralasertib (AZD6738)
- Liproxstatin-1
- Emricasan (IDN-6556)
- PMA (Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate)
- Dibutyryl cAMP (Bucladesine) sodium
- Nedisertib (M3814)
- PLX5622
- IKE (Imidazole Ketone Erastin)
- STM2457
- Saruparib (AZD5305)
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
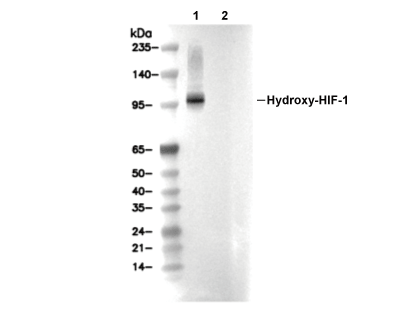
Hydroxy-HIF-1α (Pro564) Antibody [P20E16]
Cat.No.: F0384
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IF |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Monkey |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 120 kDa |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Hydroxy-HIF-1α (Pro564) Antibody [P20E16] detects endogenous levels of HIF-1α only when hydroxylated at Pro564. |
| Clone |
|---|
| P20E16 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; HIF-1-alpha; HIF1-alpha; ARNT-interacting protein; Basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS protein MOP1; Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 78 (bHLHe78); Member of PAS protein 1; PAS domain-containing protein 8; HIF1A; BHLHE78; MOP1; PASD8 |
| Background |
|---|
| Hydroxy-HIF-1α (Pro564) refers to the oxygen-dependent, trans-4-hydroxylated form of proline 564 within the oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODDD) of the 120 kDa HIF-1α subunit, a basic helix-loop-helix/PAS family transcription factor. This site-specific modification is catalyzed primarily by prolyl hydroxylase domain enzyme 2 (PHD2), which requires oxygen, α-ketoglutarate, Fe²⁺, and ascorbate, and occurs at one of two LXXLAP motifs (Pro402 and Pro564) in the HIF-1α sequence. Hydroxylation at Pro564 introduces conformational rigidity, revealing a hydrophobic core that enables high-affinity binding to the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, resulting in rapid polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of HIF-1α under normoxic conditions. This ensures that HIF-1α levels remain low and hypoxia-responsive genes are not activated when oxygen is adequate. The modification at Pro564, often in concert with Pro402 hydroxylation, acts as a molecular oxygen sensor, tightly controlling HIF-1α stability and blocking its nuclear accumulation and transcriptional activation of hypoxia-response elements (HREs) that regulate angiogenesis, glycolysis, erythropoiesis, and metastasis. Under hypoxia, PHD activity is suppressed, non-hydroxylated HIF-1α escapes degradation, accumulates in the nucleus, and initiates rapid gene induction. Disruption of this regulatory axis, whether through VHL mutations, PHD inhibition, or Pro564 mutation, results in persistent HIF-1α signaling that can drive tumor growth, vascularization, and disease phenotypes, including von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, and ischemic responses, with additional regulation by asparaginyl hydroxylation (FIH-1) and oxygen-independent pathways such as PI3K/AKT signaling. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.