research use only
GRP94 Antibody [D7B6]
Cat.No.: F4821
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC, IF, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Rat, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
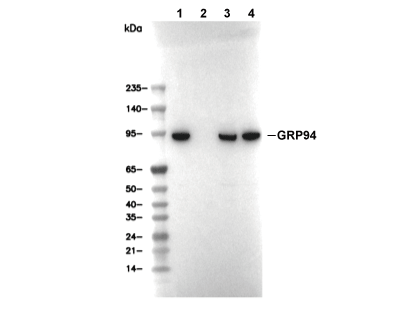
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 92 kDa 94 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Human brain tissue; Human kidney tissue; Human stomach tissue; Rat colon tissue; Mouse colon tissue; Mouse placenta tissue; Rat placenta tissue; HeLa cells; MCF7 cells; MEF cells; PC-12 cells; HEK293T cells; C6 cells; NIH/3T3 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| GRP94 Antibody [D7B6] detects endogenous levels of total GRP94 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| D7B6 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| GRP94; HSPC4; TRA1; HSP90B1; Endoplasmin; 94 kDa glucose-regulated protein; Heat shock protein 90 kDa beta member 1; Heat shock protein family C member 4; Tumor rejection antigen 1; gp96 homolog; GRP-94 |
| Background |
|---|
| GRP94, also known as gp96 or HSP90B1, functions as the endoplasmic reticulum-resident paralog of cytosolic HSP90, a glycoprotein chaperone critical for folding, maturation, and quality control of secretory and membrane proteins, including immunoglobulins, integrins, toll-like receptors, and insulin-like growth factors. Featuring four structural domains, an N-terminal nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) with ATPase activity, a middle domain (MD) for client recognition, a C-terminal domain (CTD) mediating dimerization via a conserved MEEVD motif, and a unique ER-targeting pre-neck domain (pre-N), GRP94 adopts an open "V" conformation in ADP-bound states for high client affinity and transitions to a closed twisted dimer upon ATP binding that aligns catalytic residues (Asp56, Glu121) for hydrolysis, facilitating iterative client remodeling cycles often in collaboration with BiP via direct interactions that enhance folding efficiency under ER stress. This ATP-driven mechanism ensures glycoprotein maturation through N-linked glycan coordination and calcium buffering via charged residues in its helical lid segment, activates innate immunity by chaperoning TLR clients to trigger NF-κB and IRF3 pathways for cytokine production, and supports antigen cross-presentation by dendritic cells, with overexpression in cancers stabilizing oncogenic clients like mutant EGFR/HER2 to promote tumor growth, metastasis, and therapy resistance, while deficiency causes embryonic lethality or neurodegeneration akin to Alzheimer's via tau aggregation. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.