research use only
Glutathione Peroxidase 1 Antibody [M21J11]
Cat.No.: F4831
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHP, FCM |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
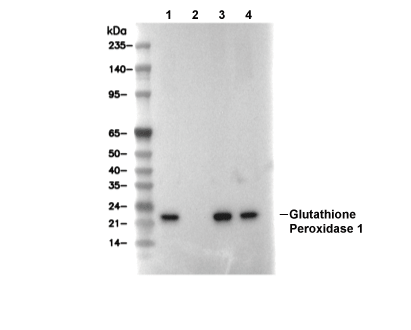
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 22 kDa 22 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
| Positive Control | Rat lung tissue; Human breast carcinoma tissue; Human fetal liver tissue; Rat liver tissue; THP-1 cells; HAP1 cells; HL60 cells; HEK-293T cells; SH SY5Y cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Glutathione Peroxidase 1 Antibody [M21J11] detects endogenous levels of total Glutathione Peroxidase 1 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| M21J11 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Glutathione peroxidase 1; GPx-1; GSHPx-1; Cellular glutathione peroxidase; Phospholipid-hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase GPX1; GPX1 |
| Background |
|---|
| Glutathione Peroxidase 1 (GPx1) is the main intracellular selenoprotein antioxidant enzyme that protects cells from oxidative damage by reducing hydrogen peroxide and lipid hydroperoxides to water and alcohols, using reduced glutathione (GSH) as an electron donor; the resulting oxidized glutathione disulfide (GSSG) is recycled by glutathione reductase. GPx1 is a homotetramer of four identical 22–23 kDa subunits, each encoded by the GPX1 gene (chromosome 3p21.31) and incorporating selenocysteine (Sec) at the active site through UGA codon recoding governed by the SECIS element in the mRNA 3′ UTR. The catalytic tetrad (Sec-Gln-Trp-Asn) resides within a pocket formed by conserved arginine and lysine residues from adjacent subunits, facilitating GSH binding and enabling ping-pong bisubstrate kinetics for efficient peroxide detoxification. Both cytosolic and mitochondrial GPx1 maintain redox homeostasis by working with superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus preventing lipid peroxidation, protein carbonylation, DNA damage, and aberrant H2O2-mediated signaling that can affect apoptosis, growth factor responses, insulin sensitivity, and Nrf2-dependent gene expression. GPx1 deficiency is linked to cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction), neurodegeneration (as shown by neuroprotection in stroke/traumatic brain injury), and cancer (where its role can be either tumor-promoting or risk-modulating, as influenced by the Pro198Leu polymorphism). GPx1 also serves as a key biomarker of selenium status and is transcriptionally regulated by Nrf2, NF-κB, and p53. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.