- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Aquaporin 5 Antibody [N15B11]
Cat.No.: F1149
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IHC |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
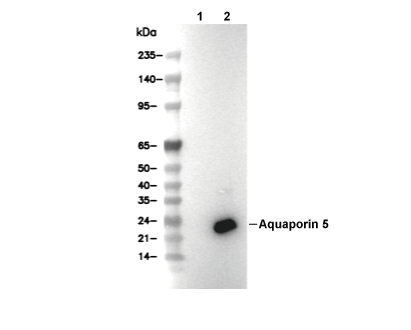
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 28 kDa 24 kDa |
| *Why do the predicted and actual molecular weights differ? The following reasons may explain differences between the predicted and actual protein molecular weight. |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| Aquaporin 5 Antibody [N15B11] detects endogenous levels of total Aquaporin 5 protein. |
| Clone |
|---|
| N15B11 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Aquaporin-5; AQP-5; AQP5 |
| Background |
|---|
| Aquaporin 5 (AQP5) is a crucial member of the aquaporin family of water channel proteins, predominantly expressed in epithelial cells of secretory tissues such as salivary, lacrimal, and sweat glands, as well as in the lungs and eye. AQP5 functions as a homotetramer, with each of its four identical monomers comprising six transmembrane α-helices and two signature Asparagine-Proline-Alanine (NPA) motifs that are essential for selective water permeability while excluding protons and larger solutes. The selectivity filter, formed by the aromatic/arginine (ar/R) constriction region, ensures high water specificity and prevents ion leakage. AQP5 mediate rapid, osmotically driven water transport across epithelial membranes, which is vital for the secretion of fluids like saliva, tears, and airway surface liquid, thus maintaining tissue hydration and homeostasis. AQP5’s activity is tightly regulated by its trafficking to and from the plasma membrane, a process modulated by intracellular calcium and cAMP signaling, as well as interactions with regulatory proteins like ezrin, which are essential for its apical localization. Dysregulation of AQP5 is implicated in several diseases: in Sjögren’s syndrome, inflammatory mislocalization of AQP5 leads to impaired saliva and tear secretion, whereas in various cancers (including breast, lung, and colon), AQP5 overexpression enhances cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis through activation of pathways like Ras-MAPK. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.