|
How to Cite 1. For In-Text Citation (Materials & Methods): 2. For Key Resources Table: |
||
|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. We strive to reply to |
Technical Data
| Formula | C21H27N7O3 |
||||||
| Molecular Weight | 425.48 | CAS No. | 937174-76-0 | ||||
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 21 mg/mL (49.35 mM) | ||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Add solvents to the product individually and in order) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
|||||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | GSK690693 is a pan-Akt inhibitor targeting Akt1/2/3 with IC50 of 2 nM/13 nM/9 nM in cell-free assays, also sensitive to the AGC kinase family: PKA, PrkX and PKC isozymes. GSK690693 also potently inhibits AMPK and DAPK3 from the CAMK family with IC50 of 50 nM and 81 nM, respectively. GSK690693 affects Unc-51-like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1) activity, robustly inhibits STING-dependent IRF3 activation. Phase 1. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
|||||||||||
| In vitro | GSK690693 is very selective for the Akt isoforms versus the majority of kinases in other families. However, this compound is less selective for members of the AGC kinase family including PKA, PrkX, and PKC isozymes with IC50 of 24 nM, 5 nM, and 2-21 nM, respectively. It also potently inhibits AMPK and DAPK3 from the CAMK family with IC50 of 50 nM and 81 nM, respectively, and PAK4, 5, and 6 from the STE family with IC50 of 10 nM, 52 nM, and 6 nM, respectively. This chemical inhibits the phosphorylation of GSK3β in tumor cells with IC50 ranging from 43 nM to 150 nM. Its treatment leads to a dose-dependent increase in the nuclear accumulation of the transcription factor FOXO3A. This compound potently inhibits the proliferation of T47D, ZR-75-1, BT474, HCC1954, MDA-MB-453, and LNCaP cells with IC50 of 72 nM, 79 nM, 86 nM, 119 nM, 975 nM, and 147 nM, respectively. Its treatment induces apoptosis at concentrations >100 nM in both LNCaP and BT474 cells. Consistent with the role of AKT in cell survival, it induces apoptosis in sensitive ALL cell lines. |
|||||||||||
| In vivo | A single administration of GSK690693 inhibits GSK3β phosphorylation in human breast carcinoma (BT474) xenografts in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Similarly, this compound induces a reduction in phosphorylation of the Akt substrates, PRAS40, and FKHR/FKHRL1. It also results in an acute increase in blood glucose, returning to baseline 8 to 10 hours after drug administration. Administration of this chemical induces reductions in phosphorylated Akt substrates in vivo, and potently inhibits the growth of human SKOV-3 ovarian, LNCaP prostate, and BT474 and HCC-1954 breast carcinoma xenografts, with maximal inhibition of 58% to 75% at the dose of 30 mg/kg/day. This compound exhibits efficacy irrespective of the mechanism of Akt activation involved. It is most effective in delaying tumor progression in Lck-MyrAkt2 mice expressing a membrane-bound, constitutively active form of Akt. |
Protocol (from reference)
| Kinase Assay: |
|
|---|---|
| Cell Assay: |
|
| Animal Study: |
|
References
|
Customer Product Validation
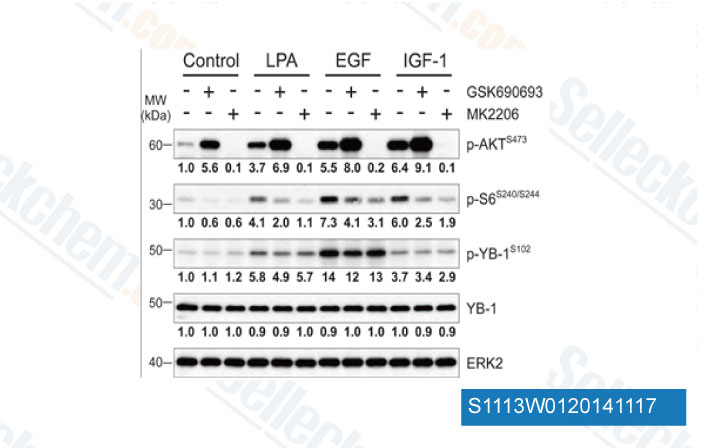
-
Data from [ Oncogene , 2014 , 33(22), 2846-56 ]
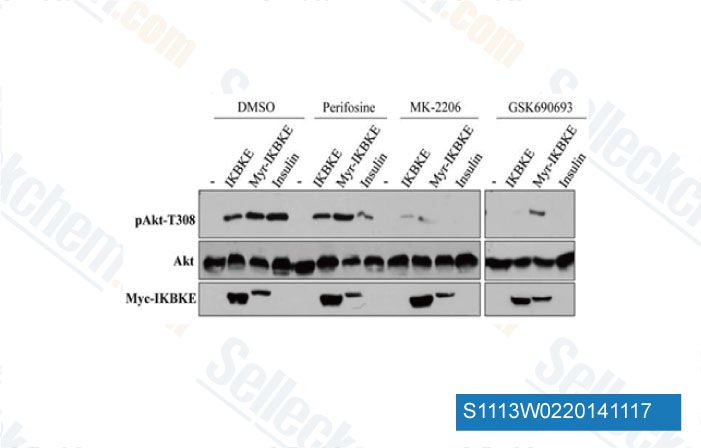
-
Data from [ J Biol Chem , 2011 , 286(43), 37389-98 ]
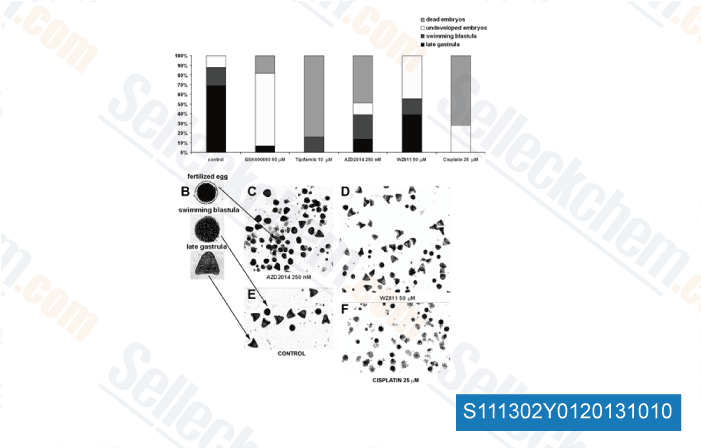
-
, , Dr. Milica Pesic from Institute for Biological Research
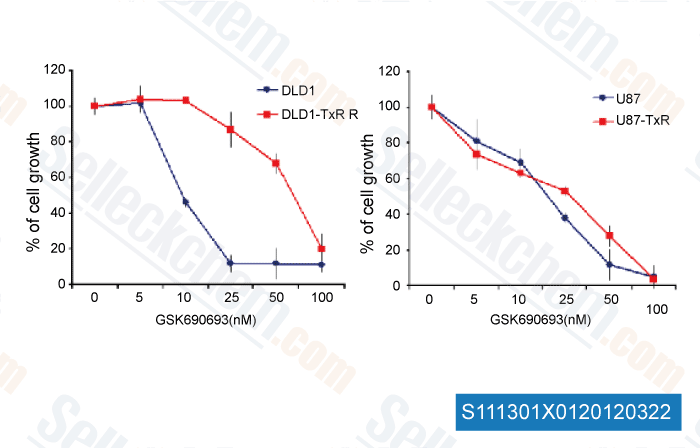
-
, , Dr. Milica Pesic of Institute for Biological Research
Selleck's GSK690693 Has Been Cited by 127 Publications
| Endothelial cell-derived SDF-1α elicits stemness traits of glioblastoma via dual-regulation of GLI1 [ Theranostics, 2025, 15(18):9819-9837] | PubMed: 41041071 |
| High fructose promotes MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma progression through NgBR-ACSS2-mediated biosynthesis of acetyl-CoA [ Cell Rep, 2025, 44(7):115947] | PubMed: 40616844 |
| Staphylococcus aureus utilizes vimentin to internalize human keratinocytes [ Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2025, 15:1543186] | PubMed: 40061451 |
| Low-Dose Perifosine, a Phase II Phospholipid Akt Inhibitor, Selectively Sensitizes Drug-Resistant ABCB1-Overexpressing Cancer Cells [ Biomol Ther (Seoul), 2025, 33(1):170-181] | PubMed: 39632683 |
| TBK1-Zyxin signaling controls tumor-associated macrophage recruitment to mitigate antitumor immunity [ EMBO J, 2024, 10.1038/s44318-024-00244-9] | PubMed: 39304793 |
| RIG-I is an intracellular checkpoint that limits CD8+ T-cell antitumor immunity [ EMBO Mol Med, 2024, 16: 3005 - 3025] | PubMed: None |
| RIG-I is an intracellular checkpoint that limits CD8+ T-cell antitumour immunity [ EMBO Mol Med, 2024, 10.1038/s44321-024-00136-9] | PubMed: 39322862 |
| Hyperglycemia-induced Sirt3 downregulation increases microglial aerobic glycolysis and inflammation in diabetic neuropathic pain pathogenesis [ CNS Neurosci Ther, 2024, 30(8):e14913] | PubMed: 39123294 |
| TMEM176B Promotes EMT via FGFR/JNK Signalling in Development and Tumourigenesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma [ Cancers (Basel), 2024, 16(13)2447] | PubMed: 39001509 |
| Kinase inhibitor pulldown assay (KiP) for clinical proteomics [ Clin Proteomics, 2024, 21(1):3] | PubMed: 38225548 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
