|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. |
Technical Data
| Formula | C9H14N4O5 |
||||||||||
| Molecular Weight | 258.23 | CAS No. | 2627-69-2 | ||||||||
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 52 mg/mL (201.37 mM) | ||||||||
| Water | 52 mg/mL (201.37 mM) | ||||||||||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | ||||||||||
| In vivo (Add solvents to the product individually and in order) |
|
||||||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
|||||||||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | AICAR (Acadesine, NSC105823, AICA Riboside), an AMPK activator, results in accumulation of ZMP, which mimics the stimulating effect of AMP on AMPK and AMPK kinase. AICAR (Acadesine) induces mitophagy. Phase 3. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||
| In vitro | Acadesine (500 μM) increases the ZMP content in extracts of isolated hepatocytes after up to 30-40 min treatment, then remains fairly constant at approximately 4 nmol/g. Acadesine (500 μM) causes a transient 12-fold activation of AMPK at 15 min in rat hepatocytes and 2-3 fold activation of AMPK in adipocytes, without affecting levels of ATP, ADP or AMP. Acadesine (500 μM) causes a dramatic inhibition of both fatty acid and sterol synthesis in rat hepatocytes. Acadesine (500 μM) also causes a dramatic inactivation of HMG-CoA reductase. [1] Acadesine induces apoptosis of B-CLL cells in a dose-dependent manner with EC50 of 380 μM. Acadesine (0.5 mM) decreases cell viability of B-CLL cells from 20 representative patients from 68% to 26%. Acadesine (0.5 mM) induces caspase activation and cytochrome crelease from mitochondria. Uptake and phosphorylation of Acadesine (0.5 mM) are required to induce apoptosis and activate AMPK in B-CLL cells. Acadesine (2-4 mM) only slightly affects the viability of T cells from B-CLL patients, Acadesine (0.5 mM) remarkedly reduces viability of B cells but not T cells. [2] Acadesine triggers loss of cell metabolism in K562, LAMA-84 and JURL-MK1 and is also effective in killing resistant K562 cells and Ba/F3 cells carrying the T315I-BCR-ABL mutation. The effect of Acadesine is abrogated by GF109203X and Ro-32-0432, both inhibitor of classical and new PKCs and accordingly, Acadesine triggers relocation and activation of several PKC isoforms in K562 cells. Acadesine dose-dependently inhibits K562 colony formation at day 10, the growth inhibitory effect of acadesine is already detected at 0.25 mM and is maximal at 2.5 mM. [3] Acadesine causes a concentration-related reduction in CD18 expression on LPS-stimulated neutrophils in vitro. [4] Acadesine significantly (1 mM) inhibits N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced granulocyte CD11b up-regulation by a mean of 61% in blood. [5] |
||
| In vivo | Acadesine (50 mg/kg) significantly reduces tumor formation in a mouse xenograft model of K562 cells. [3] Acadesine (10 mg/kg) results in higher fluid required to stabilize hemodynamics in pigs. Acadesine (10 mg/kg) inhibits LPS-induced protein permeability of pulmonary capillaries, peak inspiratory pressures on constant tidal volume and dead space ventilation in pigs. [4] |
||
| Features | A potential first-in-class ARA. |
Protocol (from reference)
| Cell Assay: |
|
|---|---|
| Animal Study: |
|
References
|
Customer Product Validation
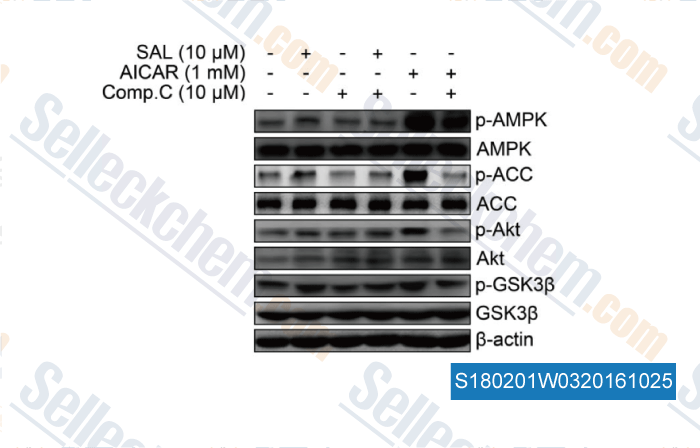
-
, , British Journal of Pharmacology, 2015, 172(13):3284–3301.
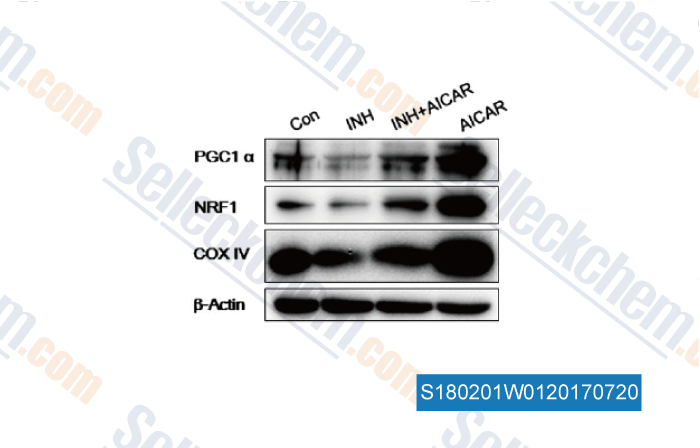
-
, , J Appl Toxicol, 2017, 37(10):1219-1224
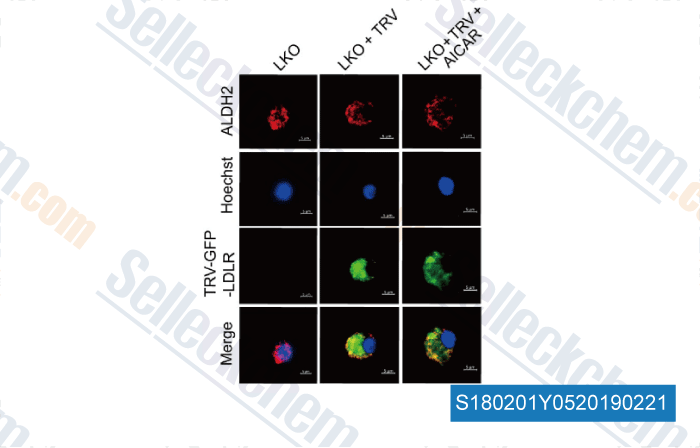
-
Data from [ , , J Clin Invest, 2019, 129(1):252-267 ]
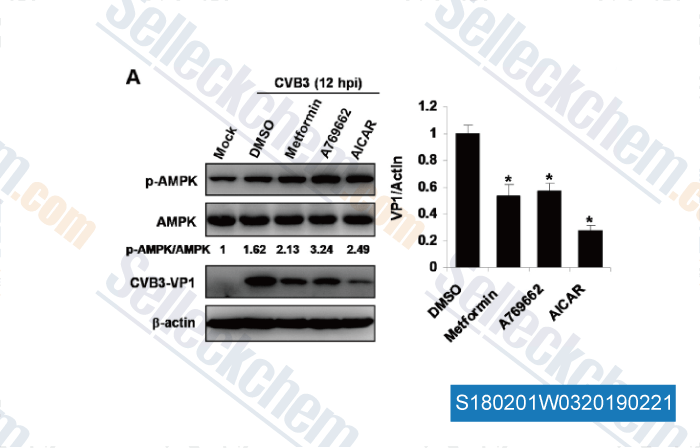
-
Data from [ , , J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2015, 85:155-67 ]
Selleck's AICAR (Acadesine) has been cited by 168 publications
| Calcium dysregulation disrupts mitochondrial homeostasis by interfering AMPK/Drp1 pathway to aggravate plaque progression and instability [ Theranostics, 2025, 15(15):7567-7583] | PubMed: 40756371 |
| Hypothalamic Astrocytes Exhibit Glycolytic Features Making Them Prone for Glucose Sensing [ Glia, 2025, 73(11):2253-2272] | PubMed: 40708167 |
| Knockdown of POLG Mimics the Neuronal Pathology of Polymerase-γ Spectrum Disorders in Human Neurons [ Cells, 2025, 14(7)480] | PubMed: 40214434 |
| Suppression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 in UMR106 Osteoblast-Like Cells and MC3T3-E1 Cells by Adipokine Chemerin [ Cell Biochem Funct, 2025, 43(2):e70051] | PubMed: 39887469 |
| Nuclear PD-L1 compartmentalization suppresses tumorigenesis and overcomes immunocheckpoint therapy resistance in mice via histone macroH2A1 [ J Clin Invest, 2024, 134(22)e181314] | PubMed: 39545415 |
| PRMT5 mediated FUBP1 methylation accelerates prostate cancer progression [ J Clin Invest, 2024, e175023] | PubMed: 39146021 |
| Brain Short-Chain Fatty Acids Induce ACSS2 to Ameliorate Depressive-Like Behavior via PPARγ-TPH2 Axis [ Research (Wash D C), 2024, 7:0400] | PubMed: 38939042 |
| Aerobic exercise suppresses CCN2 secretion from senescent muscle stem cells and boosts muscle regeneration in aged mice [ J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2024, 15(5):1733-1749] | PubMed: 38925632 |
| Metabolic regulation of misfolded protein import into mitochondria [ Elife, 2024, 12RP87518] | PubMed: 38900507 |
| Artemisinin conferred cytoprotection to human retinal pigment epithelial cells exposed to amiodarone-induced oxidative insult by activating the CaMKK2/AMPK/Nrf2 pathway [ J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1):844] | PubMed: 39285426 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
