- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly FLAG Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl
Synonyms: NSC 649890, L86-8275, HMR-1275, DSP-2033
Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl competes with ATP to inhibit CDKs including CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 with IC50 of ~ 40 nM in cell-free assays. It is 7.5-fold more selective for CDK1/2/4/6 than CDK7. Flavopiridol is initially found to inhibit EGFR and PKA. Flavopiridol HCl induces autophagy and ER stress. Flavopiridol HCl blocks HIV-1 replication. Phase 1/2.
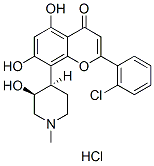
Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl Chemical Structure
CAS: 131740-09-5
Selleck's Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl has been cited by 58 publications
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.44%
99.44
Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl Related Products
Signaling Pathway
Choose Selective CDK Inhibitors
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 tumor cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of MCF-7 tumor cell proliferation | 10843211 | |||
| Mia PaCa-2 cell | Function assay | Inhibition of Mia PaCa-2 cell clonogenic assay, IC50=36 μM | 11063609 | |||
| A2780 cell | Function assay | Inhibition of A2780 cell clonogenic assay, IC50=15 μM | 11063609 | |||
| HCT116 cell | Function assay | Inhibition of HCT116 cell clonogenic assay, IC50=13 μM | 11063609 | |||
| PC3 cell | Function assay | Inhibition of PC3 cell clonogenic assay, IC50=10 μM | 11063609 | |||
| K562 human leukemia cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of K562 human leukemia cell proliferation, IC50=0.13 μM | 12190313 | |||
| MIP human colon carcinoma cell | Function assay | Inhibition of MIP human colon carcinoma cell line, IC50=0.12 μM | 12190313 | |||
| A549 human lung carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of A549 human lung carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=96 nM | 12190313 | |||
| CACO-2 human colon carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of CACO-2 human colon carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=86 nM | 12190313 | |||
| M109 mouse lung carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of M109 mouse lung carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=80 nM | 12190313 | |||
| A2780/TAX-R human ovarian carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of A2780/TAX-R human ovarian carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=78 nM | 12190313 | |||
| SKBR-3 human breast carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of SKBR-3 human breast carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=77 nM | 12190313 | |||
| A431 human squamous cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of A431 human squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=75 nM | 12190313 | |||
| LX-1 human lung carcinoma | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of LX-1 human lung carcinoma proliferation, IC50=75 nM | 12190313 | |||
| MLF mouse lung fibroblast cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of MLF mouse lung fibroblast cell proliferation, IC50=72 nM | 12190313 | |||
| PC3 human prostate carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of PC3 human prostate carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=66 nM | 12190313 | |||
| MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=66 nM | 12190313 | |||
| LS174T human colon carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of LS174T human colon carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=65 nM | 12190313 | |||
| A2780/TAX-S human ovarian carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of A2780/TAX-S human ovarian carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=65 nM | 12190313 | |||
| A2780/DDP-S human ovarian carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of A2780/DDP-S human ovarian carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=56 nM | 12190313 | |||
| OVCAR-3 human ovarian carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of OVCAR-3 human ovarian carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=54 nM | 12190313 | |||
| CCRF-CEM human leukemia cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of CCRF-CEM human leukemia cell proliferation, IC50=52 nM | 12190313 | |||
| Hs 27 human fibroblast cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of Hs 27 human fibroblast cell proliferation, IC50=51 nM | 12190313 | |||
| HL60 human leukemia cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of HL60 human leukemia cell proliferation, IC50=46 nM | 12190313 | |||
| ABAE human fibroblast cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of ABAE human fibroblast cell proliferation, IC50=45 nM | 12190313 | |||
| A2780/DDP-R human ovarian carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of A2780/DDP-R human ovarian carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=38 nM | 12190313 | |||
| HCT116/VM46 human colon carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of HCT116/VM46 human colon carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=21 nM | 12190313 | |||
| HCT116 human colon carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of HCT116 human colon carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=18 nM | 12190313 | |||
| HCT116/VP35 human colon carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of HCT116/VP35 human colon carcinoma cell proliferation, IC50=17 nM | 12190313 | |||
| LNCaP human prostate carcinoma cell | Proliferation assay | Inhibition of LNCaP human prostate carcinoma cell proliferation | 12190313 | |||
| human A2780 cell line | Proliferation assay | 72 h | Antiproliferative effect against human A2780 cell line was determined in a whole cell 72 hr cytotoxicity assay, IC50=71 nM | 15027863 | ||
| human ovarian (A2780) cancer cell | Cytotoxic assay | Cytotoxic effect on human ovarian (A2780) cancer cell line, IC50=71 nM | 15125971 | |||
| ID8 | Antiproliferative activity against | Antiproliferative activity against ID8 cells, IC50=0.007μM | 17123821 | |||
| MCF7 | Antiproliferative activity against | Antiproliferative activity against MCF7 cells, IC50=0.026μM | 17123821 | |||
| Sf9 | Inhibition of recombinant cyclin A/CDK2 expressed in | Inhibition of recombinant cyclin A/CDK2 expressed in Sf9 cells, IC50=0.012μM | 17904366 | |||
| A2780 | Inhibition of cdk-mediated NPM phosphorylation at | Inhibition of cdk-mediated NPM phosphorylation at thr199 in human A2780 cells | 18469809 | |||
| A2780 | Inhibition of cdk-mediated Rb phosphorylation at | 24 hrs | Inhibition of cdk-mediated Rb phosphorylation at thr821 in human A2780 cells after 24 hrs | 18469809 | ||
| A2780 | Inhibition of cdk-mediated Rb phosphorylation at | 24 hrs | Inhibition of cdk-mediated Rb phosphorylation at ser807/811 in human A2780 cells after 24 hrs | 18469809 | ||
| A2780 | Inhibition of cdk9-mediated RNA pol2 CTD phosphorylation at | 24 hrs | Inhibition of cdk9-mediated RNA pol2 CTD phosphorylation at ser2 in human A2780 cells after 24 hrs | 18469809 | ||
| A2780 | Inhibition of cdk7-mediated RNA pol2 CTD phosphorylation at | 24 hrs | Inhibition of cdk7-mediated RNA pol2 CTD phosphorylation at ser5 in human A2780 cells after 24 hrs | 18469809 | ||
| A2780 | Induction of apoptosis in | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human A2780 cells assessed as appearance of Mcl1 protein level after 24 hrs | 18469809 | ||
| NCI60 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human NCI60 cells after 72 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay, GI50=0.0747μM | 21080703 | ||
| NCI60 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human NCI60 cells assessed as lethal effect after 72 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay, LC50=0.904μM | 21080703 | ||
| DR-U2OS-GFP | Reduction of homologous recombination in | 0.1 uM | 56 hrs | Reduction of homologous recombination in human DR-U2OS-GFP cells expressing I-SceI nuclease assessed as reduction of RAD51 level at 0.1 uM after 56 hrs by immunoblotting | 21417417 | |
| A2780 | Cytotoxicity against | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A2780 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.023μM | 23301767 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity against | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MRC5 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.028μM | 23301767 | ||
| A2780 | Cytotoxicity against | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A2780 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.029μM | 23301767 | ||
| A2780 | Cytotoxicity against | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A2780 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.031μM | 23301767 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity against | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MRC5 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.039μM | 23301767 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity against | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MRC5 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.049μM | 23301767 | ||
| HMEC1 | Cytotoxicity against | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HMEC1 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.061μM | 23301767 | ||
| HMEC1 | Cytotoxicity against | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HMEC1 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.062μM | 23301767 | ||
| HMEC1 | Cytotoxicity against | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HMEC1 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=0.066μM | 23301767 | ||
| A2780 | Inhibition of CDK9 in | 24 hrs | Inhibition of CDK9 in human A2780 cells assessed as reduction of RNAPII CTD phosphorylation at Ser2 at GI50 concentration after 24 hrs by Western blotting analysis | 23301767 | ||
| A2780 | Cell cycle arrest in | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human A2780 cells assessed as accumulation at G2/M phase at less than GI50 after 24 hrs by flow cytometric analysis | 23301767 | ||
| A2780 | Inhibition of CDK9 in | 24 hrs | Inhibition of CDK9 in human A2780 cells assessed as downregulation of MCL1 at GI50 to 5XGI50 concentration after 24 hrs by Western blotting analysis | 23301767 | ||
| A2780 | Inhibition of CDK9 in | 24 hrs | Inhibition of CDK9 in human A2780 cells assessed as downregulation of HDM2 at GI50 to 5XGI50 concentration after 24 hrs by Western blotting analysis | 23301767 | ||
| A2780 | Induction of apoptosis in | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human A2780 cells assessed as induction of PARP cleavage at GI50 to 5XGI50 concentration after 24 hrs by Western blotting analysis | 23301767 | ||
| MT4 | Antiviral activity against | Antiviral activity against Human immunodeficiency virus 1 NL 4-3 infected in MT4 cells measured on day 4 post infection by p24 assay, EC50=0.015μM | 25914804 | |||
| MT4 | Cytotoxicity against | Cytotoxicity against human MT4 cells, IC50=0.067μM | 25914804 | |||
| Sf9 | Inhibition of CDK2/cyclin E1 (unknown origin) expressed in | 15 mins | Inhibition of CDK2/cyclin E1 (unknown origin) expressed in Sf9 insect cells using UlightCFFKNIVTPRTPPPSQGK-amide substrate after 15 mins by autoradiography, IC50=0.13μM | 25914804 | ||
| A549 | Antiproliferative activity against | 3 days | Antiproliferative activity against human A549 cells after 3 days by SRB method, GI50=0.14μM | 25914804 | ||
| DU145 | Antiproliferative activity against | 3 days | Antiproliferative activity against human DU145 cells after 3 days by SRB method, GI50=0.15μM | 25914804 | ||
| KB | Antiproliferative activity against | 3 days | Antiproliferative activity against human KB cells after 3 days by SRB method, GI50=0.16μM | 25914804 | ||
| KBVIN | Antiproliferative activity against | 3 days | Antiproliferative activity against human KBVIN cells after 3 days by SRB method, GI50=0.18μM | 25914804 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by Celltiter-Glo reagent based assay in presence of 10% fetal bovine serum, EC50=0.034μM | 26985305 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by Celltiter-Glo reagent based assay in presence of 0.625% fetal bovine serum, EC50=0.059μM | 26985305 | ||
| Sf9 | Inhibition of human | 10 mins | Inhibition of human His6-tagged CDK9/cyclin T1 expressed in baculovirus infected sf9 cells using GST-CTD as substrate after 10 mins in presence of [gamma-32P]ATP by SDS-PAGE analysis, IC50=0.0025μM | 27171036 | ||
| Sf21 | Inhibition of recombinant human | Inhibition of recombinant human full length C-terminal His6-tagged CDK9/cyclin T1 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells using PDKtide as substrate, IC50=0.011μM | 27171036 | |||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity against | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HeLa cells assessed as decrease in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, CC50=0.12μM | 27171036 | ||
| Sf21 | Inhibition of full length human | Inhibition of full length human N-terminal His6-tagged CDK6/N-terminal GST-tagged cyclin D3 expressed in sf21 cells using histone H1 substrate, IC50=0.395μM | 27171036 | |||
| Sf21 | Inhibition of recombinant human | Inhibition of recombinant human full length C-terminal His6-tagged CDK7/cyclin H/N-terminal GST-tagged MAT1 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells using cdk7 substrate peptide, IC50=0.514μM | 27171036 | |||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells assessed as growth inhibition in presence of 0.625% FBS after 72 hrs, EC50=0.059μM | 27326333 | ||
| HepG2 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HepG2 cells after 72 hrs by CelTiter-Glo assay, EC50=0.1464μM | 29407975 | ||
| KOPN8 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human KOPN8 cells after 72 hrs by CelTiter-Glo assay, EC50=0.1926μM | 29407975 | ||
| SEM | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human SEM cells after 72 hrs by CelTiter-Glo assay, EC50=0.2043μM | 29407975 | ||
| UOCB1 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human UOCB1 cells after 72 hrs by CelTiter-Glo assay, EC50=0.2084μM | 29407975 | ||
| KOPN8 | Induction of apoptosis in | 0.5 uM | 3 to 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human KOPN8 cells assessed as upregulation of cleaved PARP level at 0.5 uM after 3 to 24 hrs by Western blot analysis | 29407975 | |
| KOPN8 | Induction of apoptosis in | 0.5 uM | 1 hr | Induction of apoptosis in human KOPN8 cells assessed as upregulation of cleaved PARP level at 0.5 uM pre-treated with NAC for 1 hr and measured after 3 to 24 hrs by Western blot analysis | 29407975 | |
| insect cells | Inhibition of human | 2.5 mins | Inhibition of human CDK4/cyclin D1 expressed in insect cells after 2.5 mins by liquid scintillation counting analysis, IC50=0.02μM | 30733087 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Caco-2 | Toxicity assay | 48 hrs | Toxicity against Caco-2 cells determined at 48 hours by intracellular ATP concentration using the CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay, CC50=0.06μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Caco-2 | Function assay | 48 hrs | Determination of IC50 values for inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 induced cytotoxicity of Caco-2 cells after 48 hours by high content imaging, IC50=0.59μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Biological Activity
| Description | Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl competes with ATP to inhibit CDKs including CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 with IC50 of ~ 40 nM in cell-free assays. It is 7.5-fold more selective for CDK1/2/4/6 than CDK7. Flavopiridol is initially found to inhibit EGFR and PKA. Flavopiridol HCl induces autophagy and ER stress. Flavopiridol HCl blocks HIV-1 replication. Phase 1/2. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Flavopiridol is initially found to inhibit the epidermal growth factor receptor and protein kinase A (IC50 = 21 and 122 μM). Flavopiridol is later shown to inhibit cell proliferation, at more physiologically relevant concentrations (IC50 = 66 nM) when Flavopiridol is tested in the National Cancer Institute Development Therapeutics Program panel of 60 human tumor cell lines. [1] Flavopiridol induces G1 arrest with inhibition of CDK2 and CDK4 in human breast carcinoma cells in a time and concentration dependent manner. [2] Short time treatment of Flavopiridol (~12 hours) induce apoptosis in hematopoietic cell lines including SUDHL4, SUDHL6 (B-cell lines), Jurkat and MOLT4 (T-cell lines ), and HL60 (myeloid). [3] In the clonogenic assay, Flavopiridol functions as a highly potent cytotoxic compound with a mean IC70 with 8 ng/mL in 23 human tumor models. [4] A recent study shows Flavopiridol treatment induces a substantial AKT-Ser473 phosphorylation in human glioblastoma T98G cell line. [5] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | Recombinant CDKs Kinase Reactions | |||
| CDKs activities are determined in microtiter plates as follows. Forty μg Gst-Rb are mixed with different amounts of Flavopiridol and unlabeled ATP. Reactions are then started by the addition of an ammonium sulfate cut of the S100 fraction obtained from insect cells expressing recombinant human CDKs. The final reaction conditions are 10 mM MgCl2, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), and 1 mM DTT. The final concentration of ATP is adjusted accordingly. Radiolabeled ATP is used as a phosphoryl donor. The reaction is carried out for 2.5 minutes at 30 °C after addition of enzyme and then terminated with the addition of EDTA. The Gst-Rb is then captured with glutathione-Sepharose and the incorporated radioactivity is determined by liquid scintillation counting. | ||||
| Cell Research | Cell lines | SUDHL4, SUDHL6, Jurkat, MOLT4, and HL60 | ||
| Concentrations | 0, 100 500, 5000 nM | |||
| Incubation Time | 14 hours | |||
| Method | Cells grown at a density of 1 × 106 cells/mL are exposed to Flavopiridol for different concentrations and time periods. DNA is extracted. Briefly, cells are washed once with cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and lysed with 3 mL lysis buffer (5 mM Tris-HCL [pH 7.5]; 20 mM EDTA; 0.5% Triton X-100) for 15 minutes at 4 °C. The chromatin of the cell lysates is isolated by centrifugation (20 minutes at 26,000g, 4 °C). The supernatants containing small DNA fragments are extracted sequentially with phenol, phenol:chloroform (1:1), and chloroform. Nucleic acids are precipitated in 0.5 M NaCl, 90% ethanol at -20 °C overnight. RNA is then digested by bovine RNAaseA (60 μg/mL). After sequential reextraction and reprecipitation, DNA is dissolved in 10 mM Tris-HCL (pH 7.5), 1 mM EDTA, 0.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) before electrophoresis on 1.6% agarose gel. | |||
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | CDK2 / CDK4 / Cyclin A / p21 / p27 / Rb p-ERK / ERK / p-p38 / p-4EBP1 / 4EBP1 / p-S6 p-RNAPII / p-eIF4E / Mnk1 Cleaved caspase-8 / Cleaved caspase-9 / Cleaved caspase-3 |
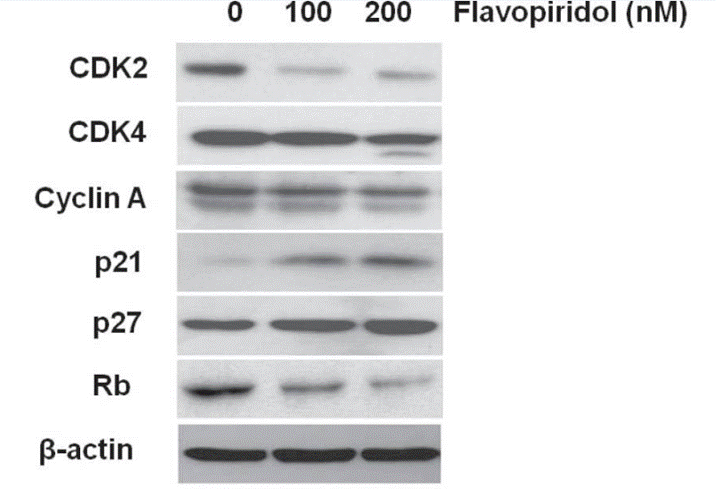
|
24572052 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
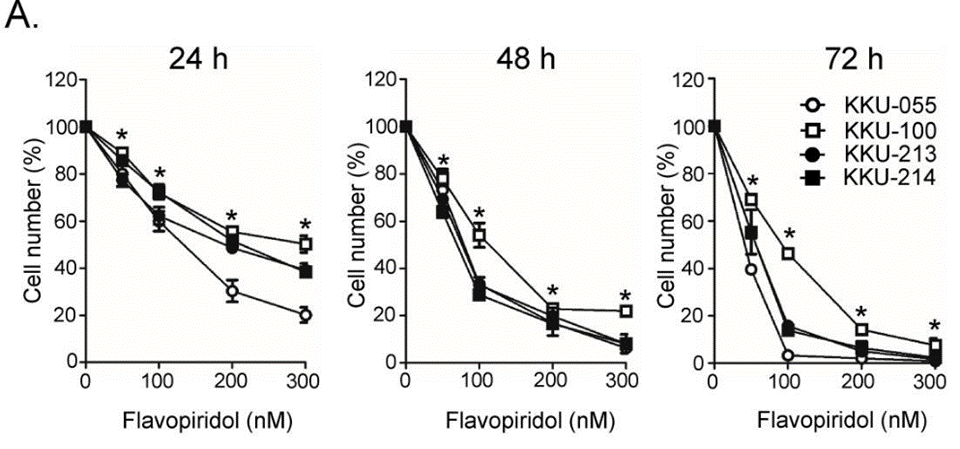
|
31193061 | |
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo | At the maximal tolerated dose of 10 mg/kg/day administered p.o. on days 1-4 and 7-11, Flavopiridol effects tumor regression in PRXF1337 and tumor stasis lasting for 4 weeks in PRXF1369. [4] After treatment with 7.5 mg/kg Flavopiridol bolus intravenous (IV) or intraperitoneal on each of 5 consecutive days, 11 out of 12 advanced stage subcutaneous (s.c.) human HL-60 xenografts undergo complete regressions, and animals remain disease-free several months after one course of Flavopiridol treatment. SUDHL-4 s.c. lymphomas treated with flavopiridol at 7.5 mg/kg bolus IV for 5 days undergo either major (two out of eight mice) or complete (four out of eight mice) regression, with two animals remaining disease-free for more than 60 days. The overall growth delay is 73.2%. Daily IV or IP administration of flavopiridol results in peak plasma levels of about 7 µM, followed by a progressive decline to approximately 100 nM in 8 hours.[6] | |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | Human prostate cancer xenografts, PRXFI337 and PRXFI369, grown s.c. in nude mice [4] Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60, human B-cell follicular lymphoma SUDHL-4, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-r |
| Dosages | 10 mg/kg/d [4]; 7.5 mg/kg/d [6] | |
| Administration | p.o.[4]; i.p. or i.v. [6] | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00112723 | Terminated | Adult Lymphocyte Depletion Hodgkin Lymphoma|Adult Lymphocyte Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma|Adult Mixed Cellularity Hodgkin Lymphoma|Adult Nodular Sclerosis Hodgkin Lymphoma|Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma|Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma|Extranodal Marginal Zone B-cell Lymphoma of Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue|Nodal Marginal Zone B-cell Lymphoma|Recurrent Adult Diffuse Large Cell Lymphoma|Recurrent Adult Diffuse Mixed Cell Lymphoma|Recurrent Adult Diffuse Small Cleaved Cell Lymphoma|Recurrent Adult Grade III Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis|Recurrent Adult Hodgkin Lymphoma|Recurrent Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma|Recurrent Cutaneous T-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma|Recurrent Grade 1 Follicular Lymphoma|Recurrent Grade 2 Follicular Lymphoma|Recurrent Grade 3 Follicular Lymphoma|Recurrent Mantle Cell Lymphoma|Recurrent Marginal Zone Lymphoma|Recurrent Mycosis Fungoides/Sezary Syndrome|Recurrent Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma|Refractory Multiple Myeloma|Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma|Stage I Multiple Myeloma|Stage II Multiple Myeloma|Stage III Multiple Myeloma|Waldenström Macroglobulinemia |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
December 2005 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT00098371 | Terminated | B-cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia|Prolymphocytic Leukemia|Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
April 2005 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00101231 | Terminated | Adult Acute Basophilic Leukemia|Adult Acute Eosinophilic Leukemia|Adult Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia (M7)|Adult Acute Minimally Differentiated Myeloid Leukemia (M0)|Adult Acute Monoblastic Leukemia (M5a)|Adult Acute Monocytic Leukemia (M5b)|Adult Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia With Maturation (M2)|Adult Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia Without Maturation (M1)|Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia With 11q23 (MLL) Abnormalities|Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Inv(16)(p13;q22)|Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia With t(16;16)(p13;q22)|Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia With t(8;21)(q22;q22)|Adult Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia (M4)|Adult Erythroleukemia (M6a)|Adult Pure Erythroid Leukemia (M6b)|Blastic Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia|Recurrent Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia|Recurrent Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia|Relapsing Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
October 2004 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00058240 | Completed | B-cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia|Recurrent Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma|Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia|Waldenström Macroglobulinemia |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
April 2003 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Chemical Information & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 438.3 | Formula | C21H20ClNO5.HCl |
| CAS No. | 131740-09-5 | SDF | Download Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl SDF |
| Smiles | CN1CCC(C(C1)O)C2=C(C=C(C3=C2OC(=CC3=O)C4=CC=CC=C4Cl)O)O.Cl | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 88 mg/mL ( (200.77 mM); Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : 37 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl | Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl supplier | purchase Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl | Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl cost | Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl manufacturer | order Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl | Flavopiridol (Alvocidib) HCl distributor