research use only
Brinzolamide Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitor
Cat.No.S3178
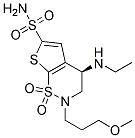
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 383.51
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Dehydrogenase HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase PPAR Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Other Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | U-104 (SLC-0111) Indisulam (E7070) Benzenesulfonamide Tioxolone 2-Aminobenzenesulfonamide |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 77 mg/mL
(200.77 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 383.51 | Formula | C12H21N3O5S3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 138890-62-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | AL-4862 | Smiles | CCNC1CN(S(=O)(=O)C2=C1C=C(S2)S(=O)(=O)N)CCCOC | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
CAII
3.19 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vivo |
Brinzolamide (< 1 mg) ophthalmic suspension lowers intraocular pressure in Dutch-belted pigmented rabbits in a dose-dependent manner with an onset within 0.5 hour and a peak response by 1–2 hours. This compound (0.6 mg) ophthalmic suspension lowers intraocular pressure in laser-treated glaucomatous cynomolgus monkeys in a dose-dependent manner with an onset within 1 hour and a peak response by 3 hours. This chemical at dosages of 30 mg/kg produces a 44% reduction in intestinal charcoal meal progression, but 1 and 10 mg/kg produced 8% and 18% decreases, respectively, in male CD-1 mice. It at 1 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and 30 mg/kg prolongs barbiturate sleep time by 57%, 15%, and 35%, respectively, in male CD-1 mice. This compound (< 3%) produces significantly greater mean percent intraocular pressure reductions and mean intraocular pressure reductions compared with placebo in patients with primary, open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. The optimal intraocular pressure-lowering concentration of this chemical is 1%, and it is well tolerated by patients with primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension when administered twice daily. It significantly decreases intraocular pressure and arteriovenous passage time compared with placebo in healthy volunteers. This compound (2%) increases optic nerve head blood flow and decreases intraocular pressure in tranquilized Dutch-belted rabbits. It (1%) reduces intraocular pressure by reducing aqueous flow and not by affecting aqueous humor drainage in normotensive eyes of rabbits and hypertensive eyes of monkeys.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































